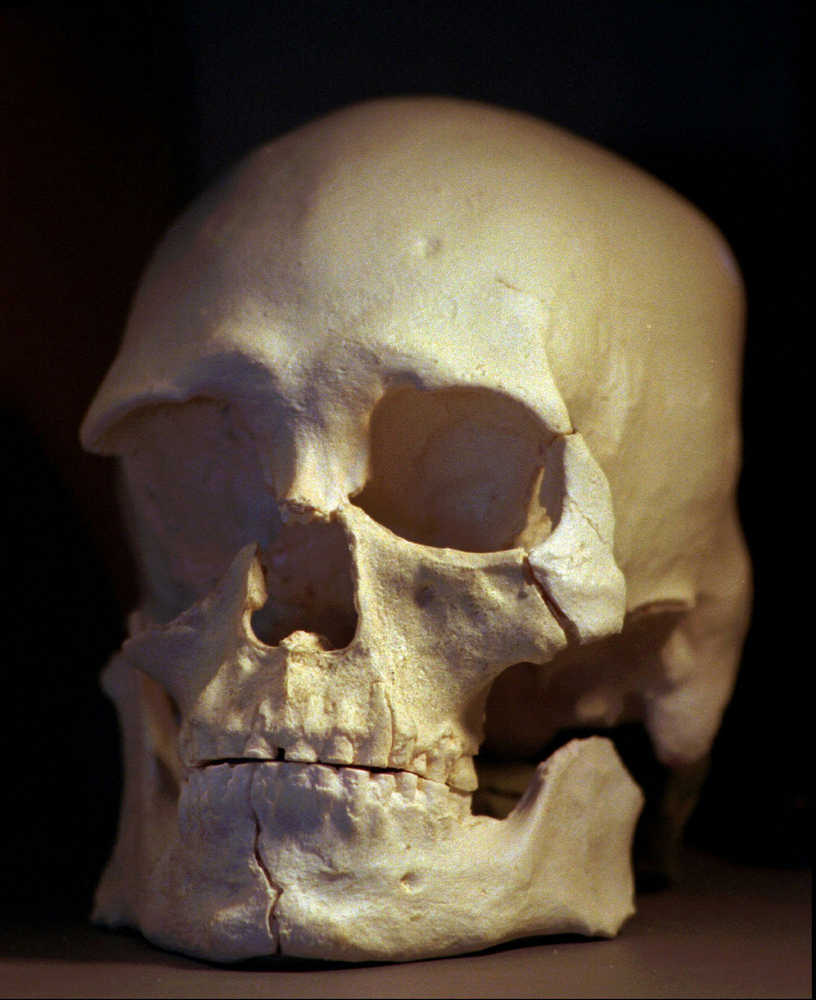
SPOKANE, Wash. — The ancient skeleton known as Kennewick Man is related to modern Native American tribes, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers said Wednesday, opening the process for returning to tribes for burial one of the oldest and most complete set of bones ever found in North America.
The Northwestern Division of the corps said its decision was based on a review of new information, particularly recently published DNA and skeletal analyses.
The corps, which has custody of the remains, said the skeleton is now covered by the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act.
The 8,500-year-old remains were discovered in 1996 in southeastern Washington near the Columbia River in Kennewick, triggering a lengthy legal fight between tribes and scientists over whether the bones should be buried immediately or studied.
The bones will remain at the Burke Museum in Seattle until the corps determines which tribe or tribes will receive them.
The next step is for interested tribes to submit a claim to acquire the skeleton for burial, said Michael Coffey, a spokeswoman for the corps in Portland, Oregon.
Determining which tribe receives the bones is likely to be a lengthy process, Coffey said. In the past, the Colville, Yakama, Umatilla, Nez Perce and Wanapum Indians have claimed a connection to them.
“We still have a lot of work to do,” Coffey said.
However, a spokesman for the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation in Oregon said the tribes plan to cooperate to hasten the burial.
“We will send in our joint request for disposition for the reburial of the Ancient One,” Sams said.
Last year, new genetic evidence determined the remains were closer to modern Native Americans than any other population in the world. Following that, the corps began to re-examine Kennewick Man’s status.
“I am confident that our review and analysis of new skeletal, statistical, and genetic evidence have convincingly led to a Native American Determination,” said Brig. Gen. Scott A. Spellmon, commander of the corps’ Northwestern Division.
Sams said the corps’ finding was correct.
“After 20 years, it acknowledges what we already knew and have been saying since the beginning,” Sams said.
Most scientists trace modern native groups to Siberian ancestors who arrived by way of a land bridge that used to extend to Alaska. But features of Kennewick Man’s skull led some scientists to suggest the man’s ancestors came from elsewhere.
Researchers turned to DNA analysis to try to clarify the skeleton’s ancestry. They recovered DNA from a fragment of hand bone, mapped its genetic code and compared that to modern DNA from native peoples of the Americas and populations around the world.
The results showed a greater similarity to DNA from the Americas than from anywhere else.